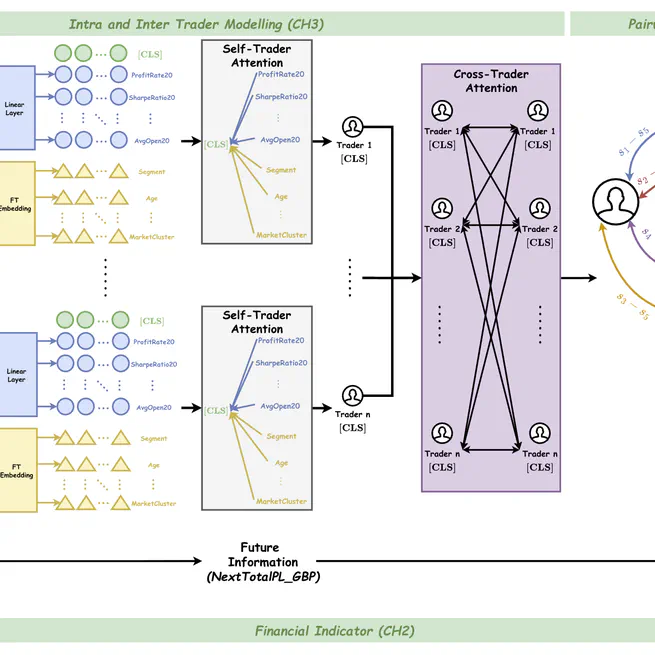
Citation @article{10.1145/3768623, author = {Li, Weixian Waylon and Ma, Tiejun}, title = {Learn to Rank Risky Investors: A Case Study of Predicting Retail Traders’ Behaviour and Profitability}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery}, address = {New York, NY, USA}, issn = {1046-8188}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3768623}, doi = {10.1145/3768623}, abstract = {Identifying risky traders with high profits in financial markets is crucial for market makers, such as trading exchanges, to ensure effective risk management through real-time decisions on regulation compliance and hedging. However, capturing the complex and dynamic behaviours of individual traders poses significant challenges. Traditional classification and anomaly detection methods often establish a fixed risk boundary, failing to account for this complexity and dynamism. To tackle this issue, we propose a profit-aware risk ranker (PA-RiskRanker) that reframes the problem of identifying risky traders as a ranking task using Learning-to-Rank (LETOR) algorithms. Our approach features a Profit-Aware binary cross entropy (PA-BCE) loss function and a transformer-based ranker enhanced with a self-cross-trader attention pipeline. These components effectively integrate profit and loss (P&L) considerations into the training process while capturing intra- and inter-trader relationships. Our research critically examines the limitations of existing deep learning-based LETOR algorithms in trading risk management, which often overlook the importance of P&L in financial scenarios. By prioritising P&L, our method improves risky trader identification, achieving an 8.4\% increase in F1 score compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) ranking models like Rankformer. Additionally, it demonstrates a 10\%-17\% increase in average profit compared to all benchmark models.}, note = {Just Accepted}, journal = {ACM Trans. Inf. Syst.}, month = sep, keywords = {learning to rank, domain-specific application, individual behaviour modelling, risk assessment} }
Sep 3, 2025
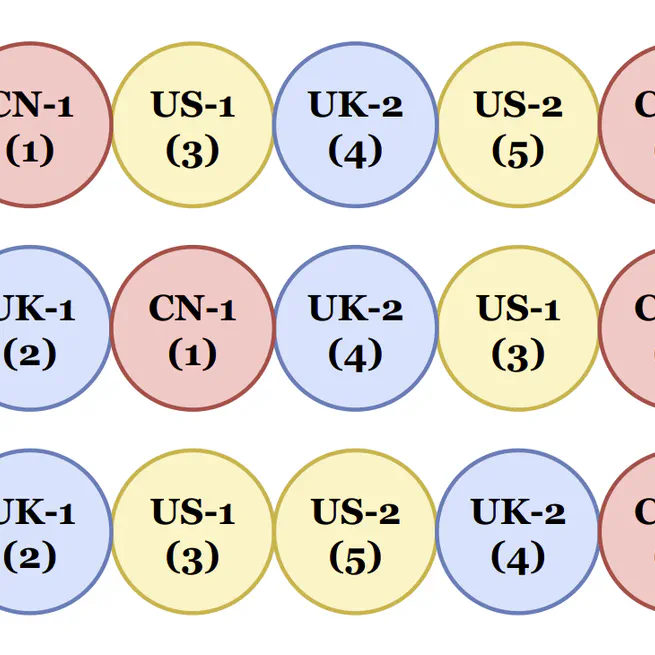
Citation @inproceedings{10.1145/3690624.3709234, author = {Li, Weixian Waylon and Ziser, Yftah and Xie, Yifei and Cohen, Shay B. and Ma, Tiejun}, title = {TSPRank: Bridging Pairwise and Listwise Methods with a Bilinear Travelling Salesman Model}, year = {2025}, isbn = {9798400712456}, publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery}, address = {New York, NY, USA}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3690624.3709234}, doi = {10.1145/3690624.3709234}, abstract = {Traditional Learning-To-Rank (LETOR) approaches, including pairwise methods like RankNet and LambdaMART, often fall short by solely focusing on pairwise comparisons, leading to sub-optimal global rankings. Conversely, deep learning based listwise methods, while aiming to optimise entire lists, require complex tuning and yield only marginal improvements over robust pairwise models. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Travelling Salesman Problem Rank (TSPRank), a hybrid pairwise-listwise ranking method. TSPRank reframes the ranking problem as a Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP), a well-known combinatorial optimisation challenge that has been extensively studied for its numerous solution algorithms and applications. This approach enables the modelling of pairwise relationships and leverages combinatorial optimisation to determine the listwise ranking. TSPRank can be directly integrated as an additional component into embeddings generated by existing backbone models to enhance ranking performance. Our extensive experiments across three backbone models on diverse tasks, including stock ranking, information retrieval, and historical events ordering, demonstrate that TSPRank significantly outperforms both pure pairwise and listwise methods. Our qualitative analysis reveals that TSPRank's main advantage over existing methods is its ability to harness global information better while ranking. TSPRank's robustness and superior performance across different domains highlight its potential as a versatile and effective LETOR solution.}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 31st ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining V.1}, pages = {707–718}, numpages = {12}, keywords = {learning-to-rank, pairwise-listwise ranking, travelling salesman problem}, location = {Toronto ON, Canada}, series = {KDD '25} }
Feb 18, 2025
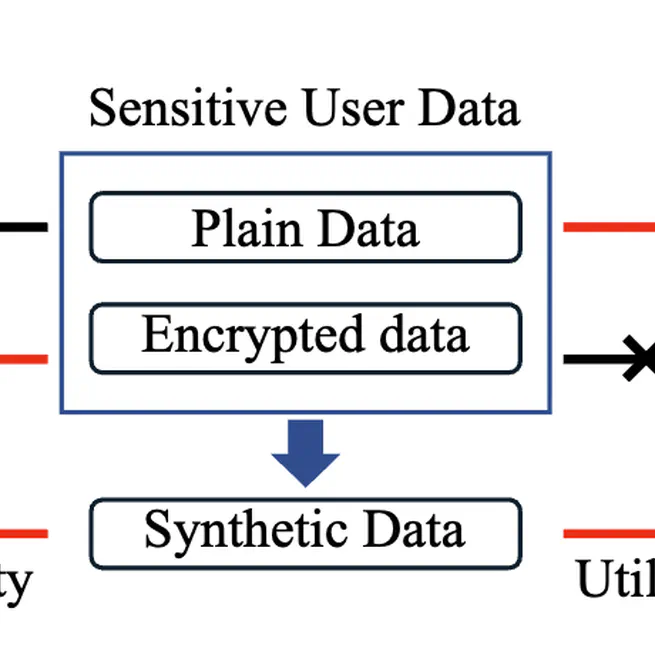
Feb 1, 2024